Running ngrok as a Service on DigitalOcean Ubuntu Server
ngrok is a handy tool that creates secure tunnels to expose local servers to the internet. It's often used for testing and debugging web applications during development. However, if you want to keep an ngrok tunnel running continuously, you'll need to set it up as a service on your server. In this tutorial, we'll walk through the steps to run ngrok as a service on a DigitalOcean Ubuntu server.
More about ngrok visit their web site -> https://ngrok.com (opens in a new tab)
Prerequisites
- A DigitalOcean Ubuntu server (https://www.digitalocean.com (opens in a new tab))
- An ngrok account (sign up at https://ngrok.com (opens in a new tab))
Step 1: Install ngrok
First, download and install ngrok on your server. You can find the instructions for installing ngrok on Ubuntu here: https://dashboard.ngrok.com/get-started/setup/linux (opens in a new tab)
Install ngrok via Apt with the following command:
curl -s https://ngrok-agent.s3.amazonaws.com/ngrok.asc \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/ngrok.asc >/dev/null \
&& echo "deb https://ngrok-agent.s3.amazonaws.com buster main" \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ngrok.list \
&& sudo apt update \
&& sudo apt install ngrokRun the following command to add your authtoken to the default ngrok.yml configuration file.
ngrok config add-authtoken <YOUR_AUTH_TOKEN>Step 2: Create a systemd Service File
Create a new systemd service file to run the ngrok command as a service:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/ngrok.servicePaste the following content into the file, replacing <YOUR_USERNAME> with your actual username and <YOUR_AUTH_TOKEN> with your ngrok authentication token:
[Unit]
Description=Ngrok Tunnel
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
User=<YOUR_USERNAME>
WorkingDirectory=/home/<YOUR_USERNAME>
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/ngrok http --domain=<YOUR_STATIC_DOMAIN_FROM_ngrok> <PORT_NUMBER>
Restart=on-failure
Environment=NGROK_AUTH_TOKEN=<YOUR_AUTH_TOKEN>
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetStep 3: Set the authentication token as an environment variable
You can set the authentication token as an environment variable by running the following command:
export NGROK_AUTH_TOKEN=<YOUR_AUTH_TOKEN>Step 4: Enable and Start the Service
Enable the service to start on boot:
sudo systemctl enable ngrokThen, start the service:
sudo systemctl start ngrokStep 5: Check the Service Status
You can check the status of the service with:
sudo systemctl status ngrok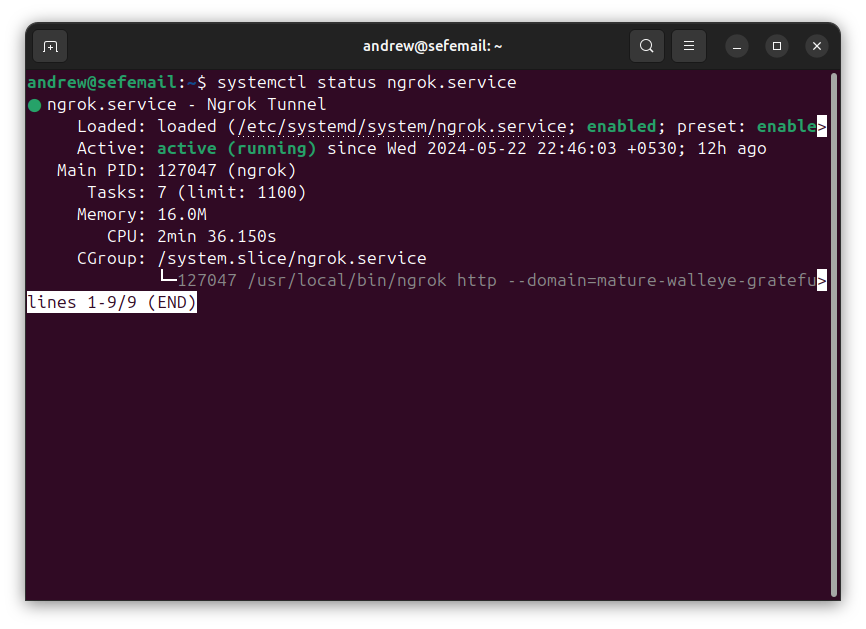
This should show you the ngrok output, including the URL that you can use to access your application.
Step 6: Access Your Application
Once the ngrok service is running, you should be able to access your application using the URL provided by ngrok, which will be in the format https://<randomsubdomain>.app
That's it! You've now set up ngrok to run as a service on your DigitalOcean Ubuntu server. Keep in mind that the ngrok URL will change every time you restart the service, so you may need to update your application accordingly. Running ngrok as a service ensures that your tunnel remains active, even after system reboots or network interruptions. This is particularly useful for testing and debugging web applications during development or for exposing local servers to the internet for specific use cases.